
There is a common belief in the sales world that the main component of sales is all about closing a deal. Contrary to popular belief though, opening a deal is equally important. When you have a good head start and can maintain the momentum throughout the deal, closing it becomes easy. Pursuing the prospect and then eventually convincing him to buy your service or product is the main deal. In between, you need to analyze the prospect’s needs, capacity, and budget to offer them the right product. And that is why lead qualification forms a significant and essential part of this process.
In this article, we will help you understand what the lead qualification process is and how to qualify leads. The following guide gives you detailed information, starting from the website visit to cracking the deal altogether. With this knowledge, you can easily qualify leads and crack sales deals.
What Is the Lead Qualification Process?
Lead qualification is the process of analyzing or evaluating a prospect’s condition based on their financial ability and interest or inclination toward purchasing your service or product. The lead qualification process includes three essential steps, which are as follows:
- Evaluating a prospect’s requirement to purchase the product or service
- Finding out if the person is authorized to take the deal forward and buy the product
- Assessing their budget and their capacity to spend on a particular product or service
What Is a Sales Qualified Lead?
Every company has a specific ICP (or ideal customer profile) for their customer base and the upcoming prospects. Every time a lead matches the ideal customer profile and is quite likely to seal a deal and purchase your service or product, they are considered “qualified leads.” As soon as they are labeled qualified—or more professionally, “sales-qualified”—they go through the seven stages of a sales cycle.
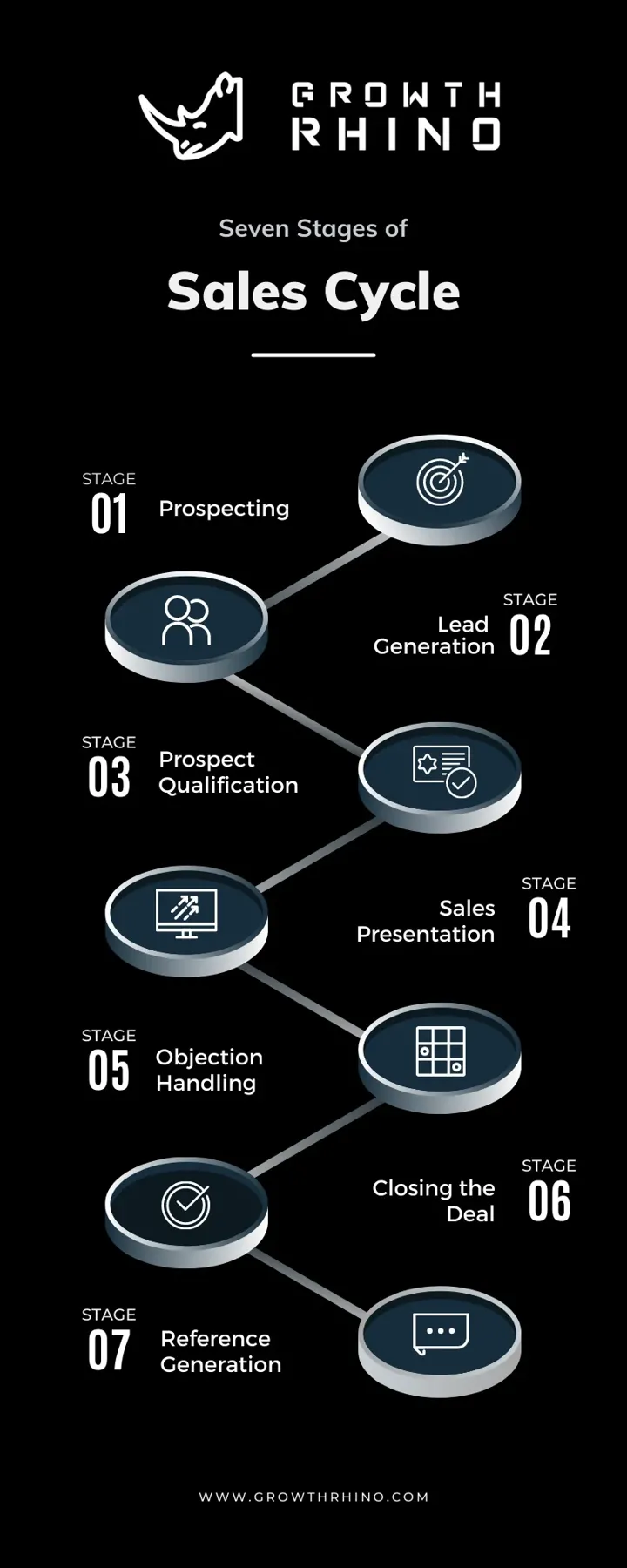
● Stage 1: Prospecting
● Stage 2: Lead Generation
● Stage 3: Prospect Qualification
● Stage 4: Sales Presentation
● Stage 5: Objection Handling
● Stage 6: Closing the Deal
● Stage 7: Reference Generation
Why Is Lead Qualification Important?
Leads are a longtime asset for every business or organization to grow and constantly boost their sales. Though these leads are considered very important for a company’s development, identifying and evaluating these leads is quite a challenging and time-consuming task. The only way to skip this difficult part and convert these leads into your customers is by qualifying them under a given set of criteria.

Sales lead qualification is crucial. It is the sole determining step toward your prospect’s interest in purchasing the product or service alongside their budget and ability to purchase it. If you know your prospect’s potential, the whole process becomes easier and quicker. Communication channels open up, and you get a clearer idea about the prospect’s approach toward engaging with your product or service.
Qualification of leads also includes segmenting these prospects into predefined categories based on several factors. It helps to create more personalized content, and the approach toward selling the product enhances.
Overall, lead qualification is an important and versatile option that lets you attract customers more smoothly and effectively with direct connection and a personalized approach. As a result, the final revenue of your organization increases substantially, with a good number of leads getting converted into customers.
What Is a Qualifying Question?
A qualifying question is a determining step where the salesperson or the marketer uses a specific question to analyze the prospect’s condition. It tells a lot about the prospect and if they are fit to be a customer. The answer explains their budget, authority, need, and many more factors enough for the salesperson or marketer to analyze thoroughly.
The lead qualification questions you ask should be open-ended, where you do not pressure the prospect for an answer. Instead your questions should help them give an honest and authentic response, enabling you to analyze their character better and move forward more smoothly. Do not jump straight to the main question; phrase it in such a manner that it seems like a part of a normal conversation.
Here are some sales qualifying questions for your reference:
- “What solutions does this product provide to solve challenges in your work?”
- “What are your budget expectations for the collaboration?”
- “What challenges have you been encountering to date to overcome the problems you are facing?”
- “How would your company succeed after you implement our service or buy our product?”
- “Would it be okay if I follow up with you on [mention a particular date]?”
What Is the Difference between Qualified Leads and Unqualified Leads?
In general, leads can be classified into two different categories: qualified leads and unqualified leads. This classification is purely based on the positioning in the sales funnel. Here is how they differ:
1) Unqualified Leads:
These leads have not been researched enough to qualify as potential customers and haven’t given any green signal regarding buying your product. There are various reasons why a lead is classified as unqualified—such as they are unsure about the offer you give them, they cannot properly afford it, or they are confused about their needs and requirements.
2) Qualified Leads:
These leads are the ones that have completely understood the advantages of your product or service. When a marketing team qualifies leads, they do it with the help of blogs, personalized emails, webinars, e-books, social media podcasts, courses, and much more. For a lead to qualify, you should always offer your products in a manner that matches their needs.
Essentially, there are three types of marketing leads, which are described below:
- IQL (or information qualified lead): IQL is also known as “cold lead” and is the fundamental step of a buyer’s complete journey. At this stage, as a provider, you should provide all the essential information about your products or services to them and get their contact details in exchange.
- MQL (or marketing qualified leads): MQL is also known as “warm lead” and is the middle stage of the complete sales funnel. These are the types of leads that have shown substantial interest in your services, eagerly submitted their contact details, have visited your website multiple times for further knowledge, and have interacted with you in various programs.
- SQL (or sales-qualified leads): SQL is also known as “hot lead” and is the final element of the sales funnel. It has undergone all the above steps and is on the brink of purchasing the product or service from you.
How to Qualify Leads: A Step-by-Step Guide to Effective Lead Qualification:
If you are looking to qualify leads for your business but do not have much knowledge, here is a detailed guide to help you out.
1) Establish an Ideal Customer Profile (ICP):
Within an ICP (ideal customer profile), you need to determine whether the buyer is a good fit and is within your target industry. You need to check if they fall into your definition of an ideal customer. To have an idea about this, add informative forms to the landing pages of your website. This particular form would collect all the relevant and required information from the visitor. Again, while you create this form to collect information, design it by keeping the ideal customer profile in mind.
You can use this information to fill out the blanks in the customer profile. If you find all the blanks filled, you can easily mark them as an ideal customer. If not, you can check for other elements and move ahead with the qualification process.
2) Start Lead Scoring:
Lead scoring is a technique many companies use to qualify leads based on a specific scale of priority. The company structures a certain scale and gives values according to the priority of the lead and their interest in the particular product or service. The score for each lead is then used to determine whether the lead is suitable to be a customer or not. It is an effective way of qualifying leads and takes a bit of research to develop the priority scale.
3) Conduct In-Depth Research:
To understand a prospect and their needs, researching them and gathering information about them is very important. You can use various analytics tools available online to track information about them. This gives you vital information about their interests, such as the following:

- Pages they like to view online
- Essential demographics
- Interests and product preferences
- Device information
Social media is another powerful tool from which you can derive the necessary and required information. It gives you advanced demographics and even psychographic information about the particular prospect and how they use every social media site and find things of their interest.
4) Use Lead Verification Frameworks to Qualify Leads:
There are a lot of sales qualification frameworks that you can use to qualify leads. You need to determine the suitable framework and put the information to derive the required outcomes. Some of them are explained below:
a) BANT Framework: The BANT framework has been a pioneer in helping qualifying leads, and it has helped thousands of companies as a starting point of the lead qualification process. Here is what the term BANT stands for and how every element of it is helpful:

- B—Budget: When you qualify a lead, one of the main factors that you need to consider before collaborating with them is whether they have the required budget to go into this venture and purchase the particular product. Various online tools can help you quickly determine the financial condition of a company, given certain factors. All you need to do is fill out the necessary metrics, and the result would help you determine whether the company has the budget to purchase your product or service.
- A—Authority: Authority is another crucial element when you are qualifying a lead. It determines whether the person you are interacting with is the decision-maker or just the medium of communication while a whole board is waiting to take the decision. Though it is quite a difficult point to analyze, it is equally essential. Again, contacting a single person is easier than interacting with a whole company.
- N—Need: Though not the most important factor in the BANT framework, it is crucial for lead qualification. Understanding their need for your service or product is necessary to understand a prospect and eventually qualify them. In most cases, when the lead is lost with their problem, or they have been using a service from a different company, and it is not helping them, they would find interest in your product and need it. They would analyze this product and have the urge to use it and solve their problem. Your job is to evaluate the lead’s needs and develop a personalized service to help them and have them as your loyal customer.
- T—Timeline: Time is a crucial factor when you are about to seal a B2B deal. Most deals take around three to four months to get completed, including every possible step. More often than not, larger deals need about six to seven months to be completely sealed. As a company, if you want to grow and measure the revenue generated from a particular deal, you need to determine a collective timeline and a limit for closing a deal. This way, you can stay accountable and work according to the timeline by finalizing maximum deals within the minimum time frame.
b) MEDDIC Framework: MEDDIC framework is another commonly used sales qualification framework by many top companies. Here is how we can break it down:
- M—Metrics: This point answers the question of how the solution you provide impacts the economy as a whole. You can get essential metric-proof points through this step.
- E—Economic Buyer: Economic buyer constitutes the person who has the authority to use the funds for purchasing the service or fund. They are the sole creator of the budget and expenses.
- D—Decision Criteria: It is the formal scale of decisive criteria that analyzes the prospect’s offerings when they need to purchase the product or service.
- D—Decision Process: This is the decisive process where the prospect analyzes the provider’s offering and selects the required one. It also includes the overall timeline of the whole deal.
- I—Identifying Pain: Here, the pain points are determined, which helps determine the need for the particular product or service. Pain points here mean the challenges faced by the lead.
- C—Champion: It is the medium that contains all the talent and ability to sell your product and keep the growth factor dynamic.
c) CHAMP Framework: The CHAMP framework is often considered as the improved and modernized version of the BANT framework and is widely used. Here is the breakdown of the CHAMP framework:
- CH—Challenges: The main point of the CHAMP framework is to determine the challenges the prospect is currently facing, for which you need to develop solutions.
- A—Authority: Just like in the BANT framework, it is important to understand who is responsible for taking the final calls. Once it is known, the process becomes a lot easier.
- M—Money: Again, like the BANT framework, the CHAMP framework also determines whether the prospect has enough budget to purchase the service or product.
- P—Prioritization: A key factor in the CHAMP framework is prioritization, and it explains the urgency of the lead in using the given solution to solve their problem and overcome their challenges.
d) ANUM Framework: The ANUM framework is an improvised version of the BANT framework. Here, if we break down each element of ANUM, we will get Authority, Need, Urgency, and Money. All these points are already covered in the BANT framework. This framework also has a lot of similarities to the CHAMP framework.
While using this framework, the designated person should focus on whether they are talking to a decision-maker from the prospect’s side. In this framework, need is considered a priority, unlike in the BANT framework. All the same components are present but are reordered according to priority.
e) FAINT Framework: The FAINT framework, when broken down, leads us to Funds, Authority, Interest, Need, and Timing. Most of the points are pretty similar to the BANT, CHAMP, and ANUM frameworks except the component of I, or Interest. This framework mainly highlights the unplanned decisions of purchase and hence does not directly concentrate on the budget. Thus, FAINT is a framework that represents a financially strong company that does not have a fixed budget but is open to spending depending upon its requirements.
f) GPCTBA / C&I: This particular framework is considered to be the longest existing acronym in the history of the sales industry. But when broken down, it gives us a vivid idea of how it works.
- Goals—what is the main priority at this point?
- Plans—what are the plans and formulations to achieve the goal?
- Challenges—what are the problems and hindrances that are halting the plans from reaching the goal?
- Timeline—what is the expected time to solve the problem?
- Budget—what expenses have been made to achieve the goal? How much more can be allocated if needed?
- Authority—what methods does a company use to purchase products and services? Who are the people involved in the decision-making before the purchase is made? What issues come up while moving ahead with the purchase?
- Consequences (Negative)—what would be the consequences if the goal is not reached? What would it cost the company?
- Implications (Positive)—what positive results would occur within the company if/after the goal is achieved?
5) Use SPIN:
SPIN is one of the oldest acronyms coined in 1988 to refer to the various situations in a sales process. The SPIN breakdown can be seen like this:
- S—the situation where the current situation of the lead is described
- P—problems faced by the prospect and how you can help to solve them
- I—implications that explain the negative impact of the problems the prospect is facing and how it is demoting them
- N—need-payoff, which explains the importance and benefits of the solution you are providing and its aftermath
A competent salesperson should always ask these four questions to the prospect in the given manner. This way, you can have an overall analysis of the prospect’s condition and can determine every possible way to help them.
6) Ensure You Have Complete Data Profiles:
If you want to qualify a lead, you need to have a complete data profile of that particular prospect to smoothen out the overall communication lines. Details like name, contact number, address, interests, demographics, and online presence are among the information that must be present mandatorily. It enables you to determine the level of engagement the prospect has with your brand and also helps you have a personalized approach toward them.

Try to have this information complete and ready. In case you missed any of these, ask for them directly during communication.
When to Move Qualified Leads through the Funnel:
Here are the steps on how you can move through the sales funnel along with your qualified leads.
- The first step is to talk to a certified person in the company who also happens to be the company’s decision-maker. This way, you could get in-depth and genuine details about the company’s condition, the problems they are facing, and the goals they aim to achieve.
- A crucial yet usually left-out step is to qualify a particular lead properly. Derive the maximum information about them while analyzing their condition before moving forward. Once the checklist has green marks and the lead is qualified and verified, you can move ahead.
- Research in detail about the lead and their condition. Only when you have relevant information can you move forward. It is also important to gather personalized information about every prospect so that you can effectively help them.
- Every time you communicate with the prospect, let them know about your next steps. Add a suitable CTA (or call to action) if possible. It not only keeps them in line but also helps you track their progress and your functions before moving ahead into the funnel.
- Keep in mind to follow up all the time. It ensures that the prospect is active and interested in your services and helps you have a step-by-step tracking of how the whole process is going.
- When you have a confirmed and qualified lead and have moved way ahead into the funnel, do not forget to attract more leads. This ensures a steady flow of leads, and you can start working on the next one as soon as you complete serving one.
Lead Qualification Checklist
Here is the list of factors that you should check while you qualify your leads.

1) Pay Attention to the Lead’s Profile:
When you go through a lead’s profile, check thoroughly whether their traits match the buyer persona that you have set. Your goal should be to divide your target audience into accessible lead segments.
2) Identify Problems and Bring Solutions:
You need to carefully analyze the pain points that indicate your customer’s problems and challenges. Furthermore, make sure to evaluate how your product or service can help them solve their problems.
3) Define Decision-Makers:
According to this step, you need to find the right decision-maker in the company with whom you are communicating. If you communicate directly with the person who makes the final call, it would be easier for you to close the deal.
4) Find Out What Your Leads Know about Your Company:
Knowing your position in the market is crucial to dealing with customers and getting in-depth knowledge about your audience. Knowing their reviews and the extent to which they are interested in you helps you adjust your services according to the audience’s needs.
Sales Qualifying: Good Signs and Red Flags:
While in the middle of the sales qualifying process, you will see both good signs and bad signs, or red flags. These are part and parcel of the journey, and here we will explain some of them.
Good Signs to Move a Prospect Forward:
Here are some common good signs within a prospect while you qualify them. As soon as you notice any of them, you can be sure to move ahead, and the chances of cracking the deal are high.
- Excuses: Excuses can be a good thing at times. When you notice a prospect giving too many excuses during a conversation, you can guess two of the following things: either the particular excuse is true and legit, or the prospect is wishing that they should have tried your solution before. One of these two confirms that the problems are real and need a cure.
- Specificity: When the prospect gives specific, direct, and quick answers to crucial questions, it means they have been thinking about their problem and need a proper solution. Again, when the prospect uses statistics to describe their pain, understand that the pain is real. In this scenario, you can legitimately move forward through the funnel with the prospect.
- Knowledge: When the prospect that also happens to be the company’s decision-maker has all the knowledge about its condition with its goals and issues, be assured that the problem is genuine. Knowledge goes hand in hand with specificity and can be relied on to judge whether to move forward in the sales funnel.
Red Flags in the Sales Process:
Here are some of the red flags to take note of during the sales qualification process. Try to avoid the prospects that come with any of these red flags.

- Inconsistency: During a conversation with a particular prospect, if you find that their answer contradicts their actions, consider it a red flag. It shows that they do not have enough knowledge about their company, which can lead to a huge deal breakdown.
- Short Answers: If an organization faces a serious problem, the authority and its employees will be in complete havoc. If they find your services suitable, they will be more than happy and interested in talking to you and sharing the issues, and your services will be a boon for them.
On the flip side, if the prospect you are talking to is not very interested and gives you short replies, consider that a red flag. It is clear from their actions that it is a total waste of time for you and their problem may not be severe enough.
Conclusion:
Now that you know how to qualify a sales lead, with practice it can become an easy job for you. Keep in mind to carry out adequate research about the prospect. It would help you crack the deal securely and smoothly. Moreover, having accurate information about the lead and their condition could also greatly help you in the future.
